¿Cómo vulnerar y auditar dispositivos IOT?
El Internet de las Cosas (IOT) facilita muchas de nuestras actividades cotidianas. Esta tecnología permite controlar cualquier dispositivo con conexión a Internet usando sólo nuestros smartphones (ya sean de Android o iOS) o una simple interfaz web; no obstante, acorde a expertos en hacking ético del Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS), la tecnología IOT aún cuenta con muchas deficiencias de seguridad, por lo que estos dispositivos son fácilmente hackeables.
A continuación se muestra HomePwn, una herramienta para controlar, detectar e incluso recopilar información para hackear dispositivos IOT, muy útil en fases iniciales de pentesting. Acorde a los expertos en hacking ético de IICS, la biblioteca predeterminada de esta herramienta puede rastrear gran cantidad de dispositivos IOT para realizar pruebas de penetración.
- Para las pruebas hemos usado Ubuntu 18.04 amd64
- Se requiere de python3.6
- Escriba sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install python3 && sudo apt-get install python3-pip
- Escriba git clone https://github.com/ElevenPaths/HomePWN.git
- Escriba cd HomePwn && ls
- Escriba chmod u+x require.txt && homePwn.py
- Escriba sudo ./install.sh; tomará tiempo instalar todas sus dependencias
- Si faltan algunas dependencias, intente ejecutar install.sh de dos a tres veces
- Escriba source homePwn/bin/activate
- Después de completar los pasos anteriores, escriba python3 homePwn.py
(homePwn) root@ubuntu:/home/iicybersecurity/Downloads/HomePWN# python3 homePwn.py
('-. .-. _ .-') ('-. _ (`-. (`\ .-') /` .-') _
( OO ) / ( '.( OO )_ _( OO) ( (OO ) `.( OO ),' ( OO ) )
,--. ,--. .-'),-----. ,--. ,--.)(,------. _.` \,--./ .--. ,--./ ,--,'
| .| |/ | | | || | | | | / | || | | |, | \| | )
| | | |( OO' .-. '| `.' | | .---'(__...--''| | | | \ | |\
| |\_) | |\| || |'.'| | (| '--. | |_.' || |.'.| |_)| . |/
`--' `--' `-----' `--' `--' `------' `--' '--' '--' `--' `--'
| .-. | \ | | | || | | | | .--' | .___.'| | | |\ |
| | | | `' '-' '| | | | | `---. | | | ,'. | | | \ |
☠ HomePwn - IoT Pentesting & Ethical Hacking ☠
homePwn >>
Created with ♥ by: 'Ideas Locas (CDO Telefonica)'
Version: '0.0.1b'
- Escriba load y luego presione TAB. Ahora probaremos algunos de los módulos de HomePwn
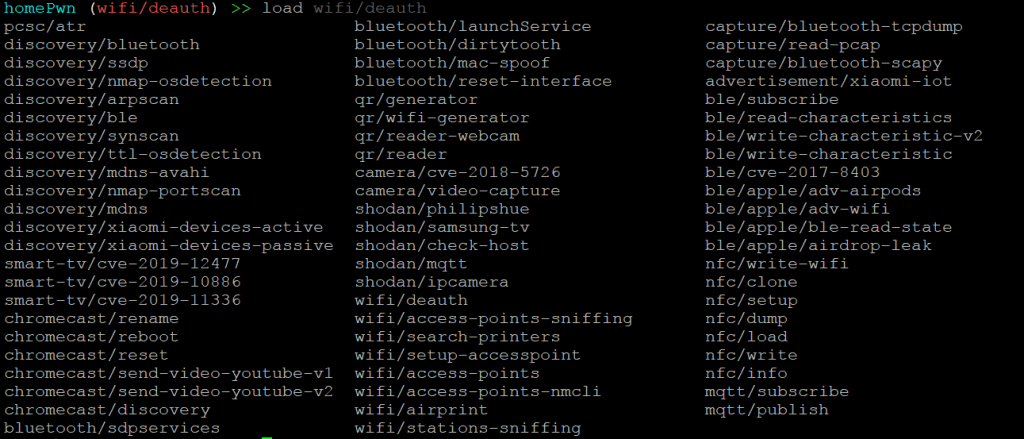
Encontrar cámaras IP
- Utilizaremos el módulo ipcamera; escriba load shodan/ipcamera
homePwn >>load shodan/ipcamera
Loading module…
[+] Module loaded!
homePwn (shodan/ipcamera) >>
- Escriba show oprtions
homePwn (shodan/ipcamera) >> show options
Options (Field = Value)
|
|_[REQUIRED] apishodan = None (Shodan API Key)
|_file = ./files/shodan_camera.txt (File to dump or read the data)
|_search = Server: Netwave IP Camera 200 OK (Camera to search)
- Escriba set apishodan
- Escriba set apishodan atjc###############4xBjrrM
- Escriba set file /home/iicybersecurity/ipcamera.txt
- Escriba set search Axis Camera && run
homePwn (shodan/ipcamera) >> set apishodan atjc###############4xBjrrM
apishodan >> atj####################4x###rrM
homePwn (shodan/ipcamera) >>
homePwn (shodan/ipcamera) >> set file /home/iicybersecurity/ipcamera.txt
file >> /home/iicybersecurity/ipcamera.txt
homePwn (shodan/ipcamera) >>
homePwn (shodan/ipcamera) >> set search Axis Camera
search >> Axis Camera
homePwn (shodan/ipcamera) >>
homePwn (shodan/ipcamera) >> run
Making request to Shodan. Search: Axis Camera 200 OK
[+] Data collected!
[+] Saving information in /home/iicybersecurity/ipcamera.txt
- Escriba exit
- Ahora ejecute cat /home/iicybersecurity/ipcamera.txt
root@ubuntu:/home/iicybersecurity# cat ipcamera.txt
72.46.55.91:8081 - Lincoln(United States)
71.81.18.38:8081 - Hoschton(United States)
114.67.66.143:9000 - China
95.126.179.83:9001 - Spain
75.74.95.74:2000 - Homestead(United States)
87.53.191.140:8081 - Frederiksberg(Denmark)
191.13.150.127:8081 - Sao Paulo(Brazil)
188.2.103.49:9001 - Novi Sad(Serbia)
93.39.181.213:9002 - Florence(Italy)
12.217.219.67:2000 - Mckinney(United States)
86.85.24.45:5001 - Eindhoven(Netherlands)
62.254.149.26:8081 - Poole(United Kingdom)
166.161.54.247:8083 - United States
166.161.54.247:8081 - United States
68.112.55.130:2000 - Hickory(United States)
82.64.29.88:8083 - France
166.251.134.252:8083 - United States
76.0.120.19:2000 - Copperas Cove(United States)
213.93.195.117:8181 - Alkmaar(Netherlands)
213.60.211.151:9000 - Orense(Spain)
84.124.168.111:8083 - Hellín(Spain)
185.62.151.139:8083 - Germany
88.2.197.210:8081 - Espera(Spain)
185.119.44.97:8081 - Amstetten(Austria)
104.244.26.200:9002 - San Francisco(United States)
128.127.19.198:8009 - Épinay-sur-seine(France)
213.162.94.8:8140 - Austria
104.244.194.130:8083 - Rochester(United States)
116.87.110.159:8081 - Singapore(Singapore)
80.15.164.219:8083 - Paris(France)
24.199.182.182:8083 - Wilmington(United States)
24.199.182.182:8081 - Wilmington(United States)
87.147.211.98:8083 - Monchengladbach(Germany)
87.139.180.12:5001 - Friedrichsthal(Germany)
24.253.12.164:9001 - Henderson(United States)
153.220.207.189:2087 - Kawasaki(Japan)
72.214.64.217:9000 - Suffolk(United States)
93.194.6.45:8081 - Rotenburg(Germany)
91.143.34.69:8083 - Odintsovo(Russian Federation)
87.245.160.250:8081 - Mytishchi(Russian Federation)
144.178.135.71:8081 - Chiclana De La Frontera(Spain)
198.182.205.201:8083 - Shreveport(United States)
88.190.82.68:8081 - Paris(France)
71.34.134.124:444 - Colorado Springs(United States)
85.66.239.195:8089 - Tabajd(Hungary)
77.237.141.141:8181 - Bolevec(Czech Republic)
87.81.2.203:8081 - Leicester(United Kingdom)
84.142.101.232:8083 - Velten(Germany)
37.209.104.88:9002 - Gomaringen(Germany)
148.56.6.24:8081 - Monzón(Spain)
61.26.16.29:5001 - Koganei(Japan)
77.119.227.125:2000 - Krems An Der Donau(Austria)
70.169.10.36:9000 - Chesapeake(United States)
91.223.240.52:8081 - France
91.192.93.38:8081 - Moscow(Russian Federation)
201.27.176.30:8081 - Sao Paulo(Brazil)
90.152.193.37:8009 - Austria
93.229.6.39:8081 - Germany
71.183.194.38:8009 - Brooklyn(United States)
204.251.179.2:8083 - United States
109.150.12.10:8083 - Bristol(United Kingdom
95.62.82.184:5001 - A Coruña(Spain)
188.107.239.126:9000 - Bad Salzuflen(Germany)
- Arriba se enumeran las cámaras IP detectadas por HomePwn utilizando la API Shodan. Para obtener más información sobre el uso de Shodan, vaya aquí
- Ahora tomaremos una IP del archivo txt anterior e intentaremos abrir una IP de cámara web de la lista. Abra el navegador y escriba 87.245.160.250:8081
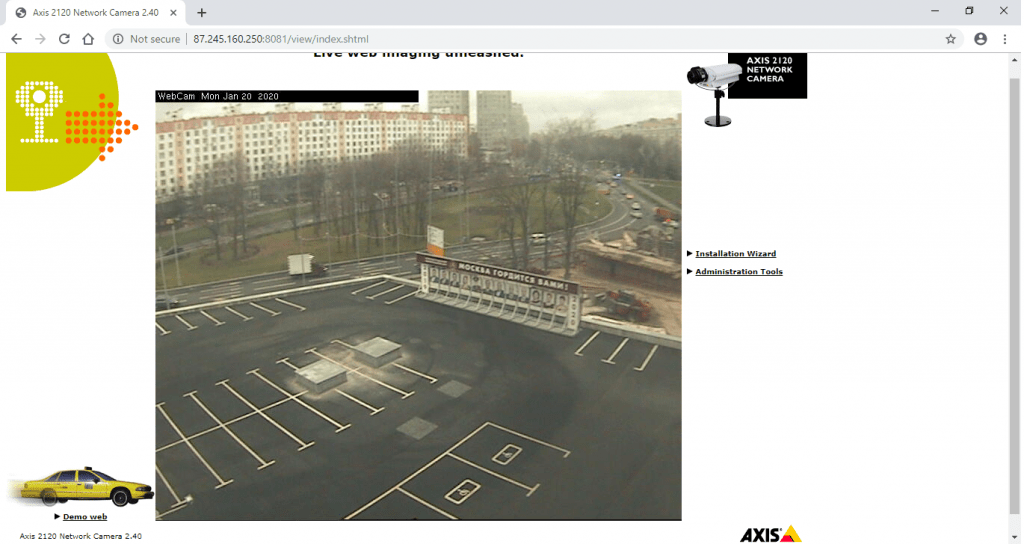
- Ahora intentemos con otra IP; abra el navegador y escriba 37.209.104.88:9002
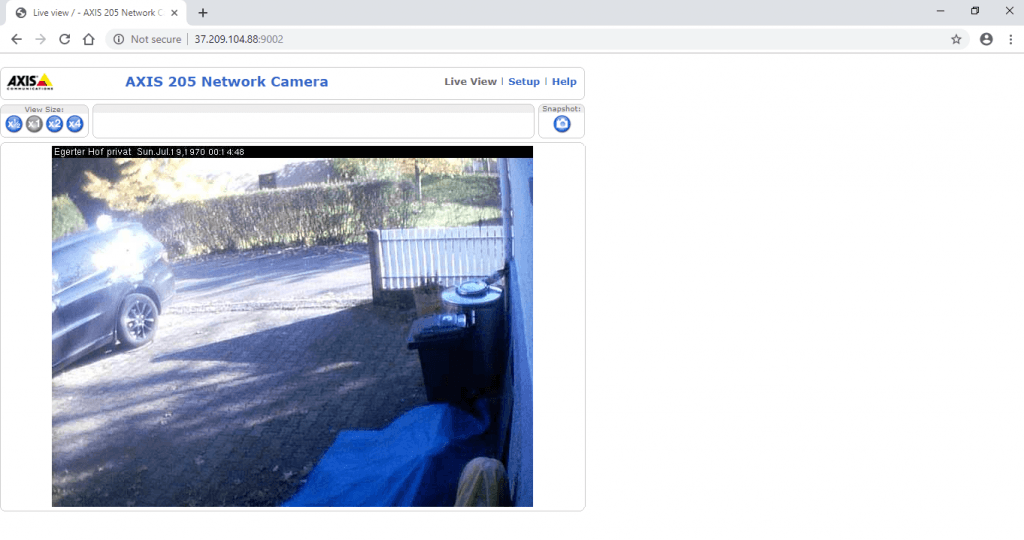
- Puede usar HomePwn con Shodan API para encontrar cámaras IP abiertas. Algunas ocasiones Shodan arrojará resultados de inmediato, otras podrá tomar más tiempo acceder a uno de estos dispositivos
Crear puntos de acceso falsos
- Escriba load wifi/setup-accesspoint
- Ahora escriba iwconfig para acceder al nombre de interfaz inalámbrica, que será necesario para el siguiente comando
- Para ejecutar en la interfaz inalámbrica, escriba set ap_iface wlxc04a0016044d
- Ahora configure otra interfaz en la cual se conecte a Internet, puede obtener esta interfaz con el comando ifconfig. Después de obtener el nombre de Internet con este comando, escriba set net_iface ens33
- Ahora configure SSID usando el comando set ssid testing
- Escriba run
homePwn (wifi/access-points) >> load wifi/setup-accesspoint
Loading module…
[+] Module loaded!
homePwn (wifi/setup-accesspoint) >>
homePwn (wifi/setup-accesspoint) >> show options
Options (Field = Value)
|[REQUIRED] ap_iface = None (The name of your wireless interface (for the AP)) |[REQUIRED] net_iface = None (The name of your internet connected interface)
|channel = 3 (Network Channel to the AP) |_sslstrip = True (Use SSLSTRIP 2.0?) |_hostapd_wpa = True (Enable WPA2 encryption?) |_wpa_passphrase = 12345678 (Please enter the WPA2 passphrase for the AP ('minimum 8 characters')) |_driftnet = False (Capture unencrypted images with DRIFTNET?) |[REQUIRED] ssid = None (AP SSID to show)
|_wireshark = False (Start Wireshark?)
|_tshark = False (Capture packets to .pcap with TSHARK? (no gui needed))
|_dnsspoof = False (Spoof DNS?)
|_proxy = False (Capture traffic? (only works with no sslstrip))
homePwn (wifi/setup-accesspoint) >> set ap_iface wlxc04a0016044d
ap_iface >> wlxc04a0016044d
homePwn (wifi/setup-accesspoint) >>
homePwn (wifi/setup-accesspoint) >> set net_iface ens33
net_iface >> ens33
homePwn (wifi/setup-accesspoint) >>
homePwn (wifi/setup-accesspoint) >>
homePwn (wifi/setup-accesspoint) >> set ssid testing
ssid >> testing
homePwn (wifi/setup-accesspoint) >>
homePwn (wifi/setup-accesspoint) >>
homePwn (wifi/setup-accesspoint) >> run
- Homepwn ofrece una manera fácil de crear puntos de acceso falsos. Tales métodos se pueden usar en técnicas como el secuestro de sesión
- Después de crear un punto de acceso falso, debe iniciar la conexión para recibir paquetes de datos habilitando el reenvío de IP. Tales escenarios son parte del curso de hacking ético impartido por el Instituto Internacional de Seguridad Cibernética (IICS)
- En otro terminal, escriba sudo sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 para reenviar la dirección IPv4
- Finalmente, puede usar Wireshark para ver la transmisión de datos
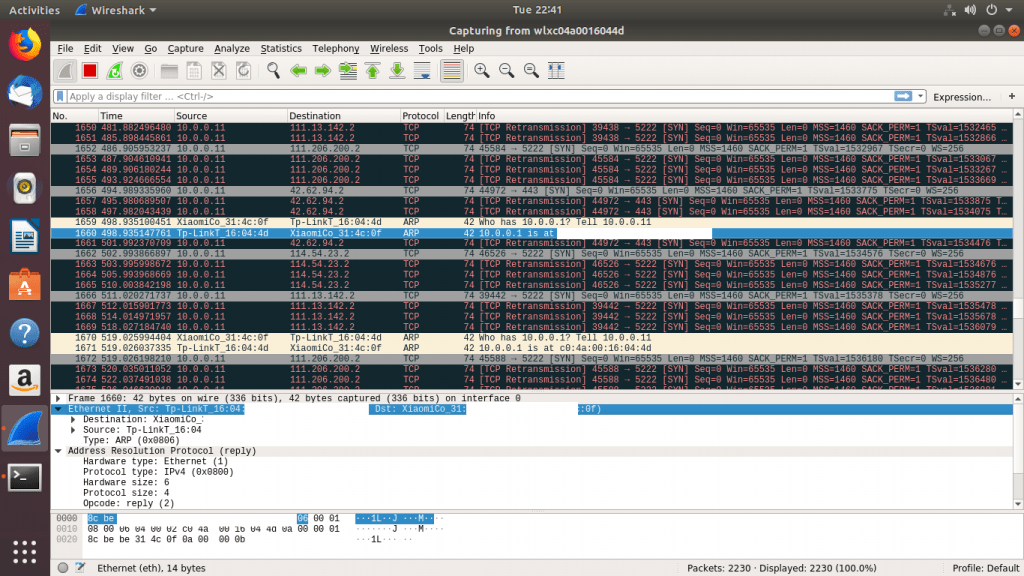
- Arriba se muestra una víctima que se ha conectado usando un dispositivo Xiaomi. También podemos ver paquetes con dirección MAC de dispositivos Xiaomi. Por razones de seguridad, hemos ocultado la dirección MAC
WiFi sniff
- Para iface, abra otra terminal y escriba iwconfig
root@ubuntu:/home/iicybersecurity# iwconfig
wlxc04a0016044d IEEE 802.11 Mode:Monitor Frequency:2.462 GHz Tx-Power=20 dBm
Retry short limit:7 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
lo no wireless extensions.
Power Management:off
ens33 no wireless extensions.
- Escriba load wifi/access-points-sniffing
- Escriba show options
- Luego escriba set iface wlxc04a0016044d
- Finalice escribiendo run
homePwn (wifi/access-points-sniffing) >> load wifi/access-points-sniffing
Loading module…
[+] Module loaded!
homePwn (wifi/access-points-sniffing) >> show options
Options (Field = Value)
|[REQUIRED] iface = None (Network Interface (that allows promiscuous mode)) |[OPTIONAL] channel = None (Network channel. Configure this option if you want to fix it and not 'make jumps')
homePwn (wifi/access-points-sniffing) >> set iface wlxc04a0016044d
iface >> wlxc04a0016044d
homePwn (wifi/access-points-sniffing) >> run
- Encontrará puntos de acceso WiFi cercanos que se pueden usar para en la detección (sniff) de WiFi o para secuestrar sesiones
[+] wlxc04a0016044d channel: 2
Access Points Enc ch ESSID
[*] 00:E0:##:3B:##:08 - Y - 2 - Cbi
[*] 18:##:F7:##:27:##C - Y - 1 - Pankaj@9212458712
[*] ##:3A:##:0B:##:08 - Y - 2 - naidus
[*] ##:95:##:BB:##:48 - Y - 4 - Worldview@arun baba
[*] E2:##:BF:##:DC:## - Y - 2 - DIRECT-yT-BRAVIA
[*] ##:1E:##:DB:##:C0 - Y - 6 - Excitel
[*] 0C:##:B5:##:B0:## - Y - 4 - MohanLalchug
- Arriba puede ver algunos puntos de acceso con su ESSID. Puede usar este módulo para detectar otras redes o buscar puntos de acceso de larga distancia. Aquí usará una smart TV Direct-yt-Bravia que será usada para detectar la IP; respecto a la televisión IP, puede ser cualquier modelo de cualquier fabricante, como Samsung, LG, SONY, entre otros
ESCANEO DE PUERTOS
- Homepwn también ofrece escaneo de puertos. Escriba load discovery/nmap-portscan
- Escriba show options
- Ahora escriba set rhost 137.74.187.100
- Escriba set rports 50-500 para escanear desde el puerto 50 al 500
- Finalmente escriba run
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | homePwn (discovery/nmap-portscan) >> show options Options (Field = Value) |[REQUIRED] rhost = None (Remote host IP) |[REQUIRED] rports = None (Remote ports (Example: 100-500)) |_timeout = 6 (Timeout to wait for search responses. (In seconds)) |_scan = S (nmap scan. Check namp scans to configure (Examples: SYN = S; Connect = T) ("show info" to check more)) homePwn (discovery/nmap-portscan) >> set rhost 137.74.187.100 rhost >> 137.74.187.100 homePwn (discovery/nmap-portscan) >> set rports 50-500 rports >> 100-500 homePwn (discovery/nmap-portscan) >> run Scanning… Host state up 'tcp' |
- Puede usar este módulo para buscar puertos abiertos de su host de destino

