API responses should be signed
I'm going to start this discussion with the why and then move on to the how. Let's begin with a couple of user stories.
As the recipient of some data, I want to verify that it hasn't been tampered with.
and
As the recipient of some data, I want to verify who originally published it.
Here's why I think this is important. We are in an era of fake news. A screenshot can be easily altered. A webpage is trivial to edit. But data should be provably true.
Recently, a prominent person's private Twitter messages were leaked. It was presented as a series of JSON files ostensibly directly from the API. But, of course, there was no way to prove the data-dump didn't contain misinformation.
If I call https://api.example.com/?id=123 myself, then I can be reasonably sure that the data has come from the server unaltered.
But what if someone emails me a JSON file? Or someone re-hosts an XML dump? Or a hacker claims to have uncovered proof of...?
As data-journalism gathers pace, it's vital to be able to see whether data is authentic.
Suppose you see a news site claiming that your favourite sports star endorses the opposing team. They have an image of a tweet. But you wouldn't trust an image of a website (I hope) without a checking a live link. Right?
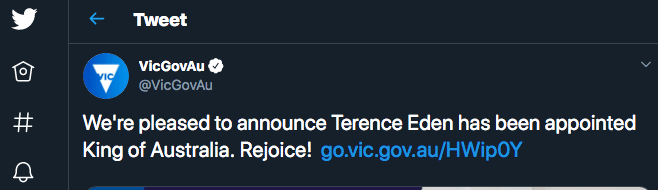
But in the data world, we get no such assurances.
Here's data from a Tweet I've just faked:
{ "created_at": "Wed Oct 10 20:19:24 +0000 2018", "id": 105011862119892123, "text": "Terence Eden is now officially the King of Australia", "user": { "id": 6253282, "id_str": "6253282", "name": "Australian Government", "screen_name": "AusGovOfficia1", I've just made that up. But you've got no way to prove that it did not come from Twitter. Perhaps it was a real Tweet which was subsequently deleted?
Where this matters
Do you rely on data for your job? If someone gives you a scrap of data claiming to be from a website, how can you prove it is authentic?
Perhaps a Police API tells you what the crime rate is, or a betting API tells you what the odds are, or a news API tells you who was convicted of a crime. Or a source leaks information from a social network. How can you prove that the data is authentic and unaltered? Or someone else could present false data as coming from a trusted source. Or a trusted source could publish fake data and later claim they didn't.
Here's the end result that I want.
- Given a piece of data,
- Prove that where it came from and,
- Prove that it hasn't been altered.
How to do it
This is where I get stumped. I can clearly see the need for this. Disinformation is an attack on civilisation. But I can't see how to do it in a seamless and easy to understand way.
There have been lots of proposals for how to do this.
I think it boils down to three distinct design choices.
- Keep the signature and the message separate.
- Include the signature in the message.
- Only sign part of the message.
Separation of Powers
The first is conceptually easiest.
- The API call
example.com/?id=123returns some JSON containing the data requested. - The API call
example.com/?id=123&signed=truereturns the signature only.
It relies on a few assumptions. Mostly that a GET operation is idempotent in terms of what it returns. That is, the data returned from a query is always the same.
It reduces complexity for the server and client. If the client doesn't care about verification, the server doesn't have to calculate it.
It might be complicated to store the information. You would need to keep response.json and response.signed.json as separate files.
It might be fragile. If a single bit or byte of the data is altered - say tabs get converted to spaces - then the signature could become invalid.
If you want someone to verify an API response, they need two separate files and need to load them in the right order into any verification system. Again, not an impossible task, but might make things more complicated than necessary.
Inclusivity
Does the set of all sets include itself? This isn't just a philosophical problem. If a signature is included in a response, does the signing process have to take account of the signature?
The usual way around this is to encode the result first. So, imagine your API response was BASE64 encoded and then signed. It might look like this:
{ "response": "data:text/plain;base64,SGVsbG8sIFdvcmxkIQ%3D%3D...", "signature": "0f60066673e0de...." } That keeps the document and signature together, but does have some disadvantages.
It loses the human-readable nature of the response. It also means that your code has to BASE64 decode the response before interpreting it. Both of those are annoying for debuggers - but not critical issues.
Partial
What if we only sign the critical parts of the response, rather than all the metadata? This is perhaps the easiest to implement, but has some drawbacks.
{ "created_at": "Wed Oct 10 20:19:24 +0000 2018", "id": 105011862119892123, "text": "Terence Eden is now officially the King of Australia", "text-sig": "0f60066673e0de....", ... That is, only sign the text. Or perhaps text + ID. Or any useful subset of the API response. It's simple to parse for humans and computers. But the metadata might be a crucial part of the information we want to verify. Knowing the date something was published, for example, could be as important as the content itself.
Put it all on the blockchain!!!!!
No.
Well... OK. Maybe this is a use for a Merkle Tree or similar. If every API response has an ID, then a cryptographic hash could be appended to a public ledger. But that has all the disadvantages of the previous schemes without any real benefit.
Security is hard
The problem with all of the above approaches is that the API provider needs to safely and securely manage cryptographic keys. That's expensive and complicated. If an attacker got access to the keys, they could issue fake statements.
But, the good news is that the tech tech is here and it works. JOSE is a suite of specifications - including JSON Web Tokens - which are well used across the Internet. Mostly for signing OAuth logins.
So, can we use it?
Will anyone care?
I suppose this is the crucial question. Right now I can easily fake a screenshot and the majority of people won't even look to see if the information is true - no matter how incredible the claim is.
But we need to build a better foundation for the future. One where information brokers can say "I have proof that this exact data came from this specific website at this precise time."
We have to believe that truth and trust are important.
from Hacker News https://ift.tt/36182Pf